The change agent teaching model
Although societal impact is incorporated in Utrecht University’s education, a framework for its creation is missing. Such a framework defines learning processes and outcomes for making societal impact, supporting teachers in selecting didactical approaches and students in identifying the relevant knowledge and skills. This project develops a framework through a systematic literature review.
Background information
Universities are increasingly expected to contribute to solving large societal challenges, requiring new ideas, technologies and societal arrangements. The creative and entrepreneurial agents behind these innovations can be seen as leaders of (societal) change, also known as change agents. These change agents need to have the values, knowledge and skills to successfully realize social change. Through dedicated teaching programs and extracurricular initiatives, Utrecht University aspires to educate such leaders.
Project description
There are four strands of literature relating to change agent education: leadership of social change, sustainable leadership education, social entrepreneurship education, sustainable entrepeneurship education. Since a comprehensive framework in which the aspects of change agents (values, knowledge and skills) come together is currently lacking, this project conducts a systematic literature review by comparing the different strands of literature with respect to their emphasis on the aspects of change agents.
Aims
This project aims to develop an evidence-based comprehensive framework on the concept of change agents, learning outcomes, learning processes, associated didactical approaches. In addition, this project aims to draft a research agenda on change agent education.
Results & Conclusions
Results show that the different strands of literature share the aim of educating change agents in authentic, collaborative learning processes that are experiential and challenge students to create value for others. Whereas social and sustainable entrepeneurship education focuses more on creating societal value, sustainable leadership education captures the personal development of students. Based on the review, an overarching teaching model for educating change agents was developed (Figure 1).
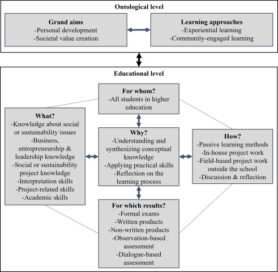
Figure 1. Teaching model for change agents
References
- Astin, H. S. (1996). Leadership for social change. About campus 1(3), 4–10.
- Compagnucci, L. & Spigarelli, F. (2020). The Third Mission of the university: A systematic literature review on potentials and constraints. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 161.
- (2018) The future of education and skills: Education 2030. OECD Education Working Papers.
- Pache, A. C. & Chowdhury, I. (2012). Social entrepreneurs as institutionally embedded entrepreneurs: Toward a new model of social entrepreneurship education. Academy of Management Learning and Education, 11(3), 494–510.
- Shriberg, M. & MacDonald, L. (2013). Sustainability leadership programs: Emerging goals, methods & best practices. Journal of Sustainable Education, 5, 1–21.
- Tiba, S., van Rijnsoever, F. J. & Hekkert, M. P. (2018). Firms with benefits: A systematic review of responsible entrepreneurship and corporate social responsibility literature. Corporate Social Responsibility Environmental Management, 26(2), 265–284.
- Utrecht University. (2020) Open mind, open attitude, open science – Improving the world sustainably together – Strategic Plan 2025.
- Van Rijnsoever, F. J. & Deuten, J. Start-ups met idealen Over ecosystemen voor start-ups met maatschappelijke impact.
- Van Rijnsoever, F. J., Sitzler, S., & Baggen, Y. (2023). The change agent teaching model: Educating entrepreneurial leaders to help solve grand societal challenges. The International Journal of Management Education, 21(3).
Interesting attachments
- Click here for the journal publication
